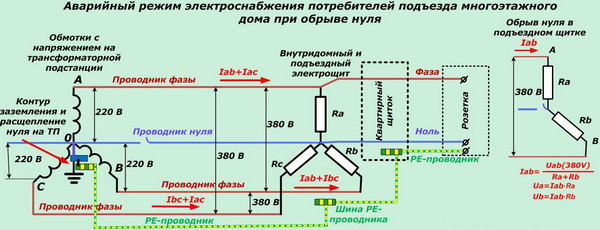
A break in the neutral wire in a three-phase circuit (or its burnout) is a common phenomenon familiar to most specialists and operating personnel of substations. He is also faced by electricians serving apartment buildings, in which this damage occurs at the entrance to the riser or directly in the apartment. It usually manifests itself as a break in the "earthen" vein. To understand the essence of the phenomenon, you first need to understand the reasons for its occurrence.
Formation of supply circuits and causes of breakage
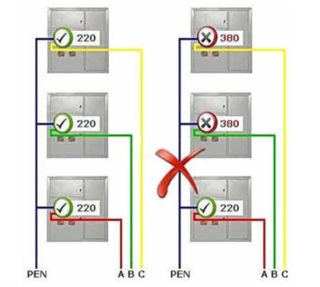
The principle of formation of 380 Volt supply circuits is based on the fact that each phase is connected to "its own" group of consumers (houses, entrances or apartments). A zero break in three-phase networks occurs when the distribution of loads is disturbed, connected, like the windings of the station transformer, according to the "star" scheme - they must be connected evenly. With the correct distribution, the current components are mutually compensated, and the total value in the neutral wire is close to zero. Therefore, the neutral conductor is made of a smaller section than the phase wires - theoretically it can be excluded altogether, since the current should not flow here.
Any deviation from this requirement leads to phase imbalance and the appearance of parasitic currents in the neutral conductor.
Since on the consumer's side the number of switched on household appliances and bulbs per phase can be arbitrary, not a single supply line can do without a deviation from the norm.
A current always flows through the neutral wire, slightly displacing the phase nodes in one direction or another. In the corresponding diagrams, it looks like the approach of the zero point to one of the phases. If the cross-section of the neutral wire in the supply networks is severely skewed, it may not be enough to withstand the increased current through it. Over time, constant overloading leads to its burning.
When switching from three-phase circuits to linear branches (their formation occurs at the entrance to the access riser), the situation is completely different. Problems with zero burn-off in single-phase networks can arise for the following reasons:
- Poor contact or damage to the neutral conductor on the linear branch. He settles down on the entrance switchgear of the entrance.
- Loss of the corresponding contact in the floor panel. In some houses, it is installed on every site.
- Violation of connections in the "earth" wire at the entrance to the apartment or inside it.
The malfunction first manifests itself as a short-term loss of electricity, the cause of which cannot be found immediately. Over time, when the contact at the point of connection of the zero core completely collapses, household appliances will completely stop working, and the light will turn on.
Possible consequences
The consequences of a zero break in a three-phase network are sometimes extremely dangerous. Regardless of the grounding system used, when the zero conductor burns out, high potentials appear in apartments connected to such a cable. Due to a strong skew, voltages reaching 380 volts will appear on some wiring lines. On other branches from the 3-phase input, on the contrary, they can drop to almost zero.
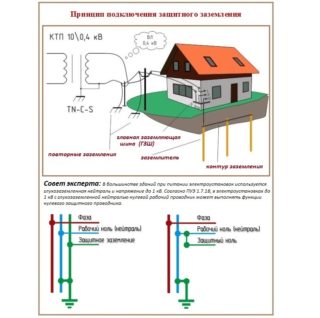
Breaks in the neutral wire are dangerous because, first of all, they pose a threat to household devices connected to sockets.This can threaten the complete failure of expensive equipment or the fire of the old aluminum electrical wiring, which can lead to a fire. On the other hand, if the house is connected via a TN-C system with combined PE and N conductors, a break in the common PEN conductor will lead to the loss of the protective function against electric shock. In the absence of re-grounding, the consumer will be defenseless if the PEN wire breaks, even if an RCD is installed in his apartment, which will not be able to work without a zero core.
If a zero break occurs on one of the apartment lines protected by a separate machine, first of all, all electrical devices connected to it will stop working. In addition, if there is no zero and there is a phase in the network, the dangerous potential of 220 volts through constantly connected loads will fall on the ground terminal. As a result, there will be one more phase in the outlet, which is very dangerous in the absence of normal grounding.
In case of any accidental breakdown of insulation in the washing machine, for example, the dangerous potential will have nowhere to drain, since the earth wire is cut off. For a consumer standing on a concrete floor connected to the ground, this poses a great danger, since all the current will flow through it.
Protection against burnout or zero break
The study of the consequences of violations in the operation of three-phase lines and their branches showed that it is necessary to take some measures to prevent these phenomena. Reliable protection against zero break in a single-phase network allows:
- keep household appliances intact;
- to ensure the protection of the user from electric shock;
- to prevent accidental ignition of worn-out electrical wiring and the outbreak of fire.
To protect against phase loss, modern electrical equipment is used, which include special relays, as well as line overload protection devices (SPDs). The first ones are available in two versions, one of which is intended for 3-phase circuits, and the second allows you to protect single-phase branches. The principle of their operation consists in instantaneous disconnection of the supply network in case of voltage deviation in it in excess of the established norm.
The second device for protection against phase loss is usually used in private households in order to disconnect loads in the event of a dangerous situation. Its principle of operation is to reduce the conductivity of internal circuits with significant potential drops. The most effective way to prevent dangerous consequences in three-phase networks is to use re-grounding, the device of which in apartment buildings is associated with great difficulties.
In rural areas and private suburban buildings, this approach is very simple to implement. It is enough to equip a grounding device in the area adjacent to the house and connect it via a copper bus to a separate contact mounted in the lead-in box.
As another means capable of protecting against a break in the zero core, you can use a residual current device or, in short, an RCD. Its kind is a differential device that combines the functions of an RCD and a typical machine. For these purposes, ordinary products are not suitable, which necessarily need a whole zero core for normal operation. It is allowed to install in branch lines only those devices in which the function of protection against zero break is specially provided.