Fluorescent lamps are lighting fixtures that save energy compared to conventional light sources. Fluorescent lamps are used to illuminate residential, work and industrial premises. Their work is based on the effect of luminescence. To choose the right light bulb, you need to know the design features and specifications.
Principle of operation

A fluorescent lamp is a gas-discharge light source. Radiation occurs due to the reaction of the mixture of gases in the flask. Previously, such devices were practically not used in a domestic environment, since it was believed that they could harm eyesight. But after conducting research, scientists came to the conclusion that the rays are perfectly perceived by the human eye. What a fluorescent lamp consists of depends on its purpose. The mixture of vapors inside may vary.
Structurally, the device is a glass tubular flask, on the inner surface of which a phosphor is applied. Electrodes are located at the ends. Inside the tube - mercury vapor and a mixture of gases.
The principle of operation of a fluorescent lamp is as follows:
- Under the action of an electric field, a gas discharge occurs in the bulb.
- The current that passes through the vapor causes ultraviolet radiation, which causes the phosphor to glow.
The bulb is made of glass, which does not transmit UV rays, but gives only visible light. An exception is bactericidal lamps, which require the emission of ultraviolet radiation.
Advantages of fluorescent fluorescent lamps:
- high luminous efficiency;
- saving electricity;
- strength - high-quality materials are used for the manufacture of shades;
- duration of work;
- variety of shapes and sizes;
- wide range of color temperatures;
- creates warm natural light similar to daylight.
Disadvantages:
- the presence of harmful components in the llama (mercury);
- the complexity of disposal;
- restrictions on the number of on and off cycles;
- sensitivity to moisture;
- full inclusion does not occur immediately;
- may buzz and flicker during operation;
- dependence of stable operation on temperature.
The optimum operating temperature of the device is +20 degrees. The allowable range is 55 degrees, but it is constantly expanding with the development of technology and the use of electronic ballasts.

The cost of fluorescent light bulbs is lower than that of LEDs. But it is more than incandescent or halogen lamps.
Varieties of fluorescent lamps
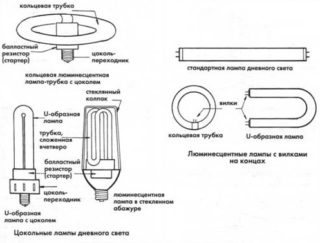
The classification of fluorescent lamps can be carried out by power, temperature, shape, installation method, length. The most common are high and low pressure lamps. High pressure appliances are used on the streets and in high power luminaires. Low pressure bulbs are suitable for chandeliers in residential and industrial environments.
By the type of installation, light sources are classified into the following groups:
- suspended;
- portable;
- ceiling;
- wall.
By the structure of the lamp there are:
- compact;
- ring;
- U shaped;
- straight lines.
Most often, an annular and straight short or long lamp is used for lighting.Devices powered by rechargeable batteries or batteries are also actively used.
Application area

Fluorescent lamps are widely used due to their advantages. They are used for lighting in houses and apartments, offices, factories and warehouses, in street lighting and illuminated advertising.
Depending on the color rendering spectrum, lamps are:
- similar to solar radiation - used in the lighting of offices, production shops, administrative organizations;
- High color rendering - suitable for exhibitions, galleries, museums, hospitals, dyes, textiles, and other art supplies;
- with increased radiation in the red and blue spectrum - used to illuminate aquariums, greenhouses, plant stores, greenhouses;
- with a shift in the blue and UV part of the spectrum - decorating aquariums;
- light in the UV spectrum - tanning beds;
- High power UV radiation - antibacterial lamps.
Before the active use of LEDs, fluorescent luminous bulbs were used to illuminate liquid crystal monitors. Powerful fluorescent devices are used in street lighting of tracks, stadiums, and grounds.
Specifications
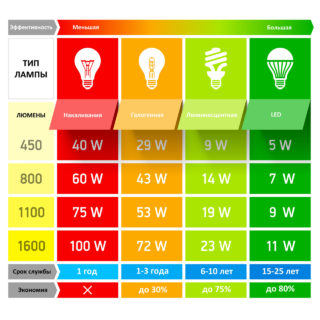
The main technical characteristics include:
- Color rendering. This is one of the main characteristics of a light source. Determined by the composition of the phosphor. Fluorescent devices have a wide range of colors due to the many different compositions. The most common for home use are devices with a color temperature of 2700 K, giving a warm natural hue. In advertising and architectural lighting, devices of different colors are used - pink, blue.
- Base / plinth. It is possible to distinguish 2 forms of the base, depending on the design - pin and cartridge. Pin bases are used in luminaires in which a U-shaped bulb is installed. The cartridge bases have a classic appearance with different thread diameters. They are used in home lighting fixtures.
- Voltage. The working power is 220 V, less often a serial connection of spirit lamps is used, operating at 127 V.
- Power. The most common are 18V lamps. There are more powerful sources for floodlights, reaching 80W.
- Life time. Can reach 40,000 hours.
- The efficiency is above 20%.
- Physical dimensions. For example, Armstrong lamps have standard dimensions for a cell of 600x600 mm.
- Degree of protection against dust and moisture. Determines the ability to work safely under certain climatic conditions.
- Manufacturing material. Plastic, metal and others.
When choosing a lamp, you need to take into account the technical characteristics, as well as the parameters of the luminaire in which the light source will be installed.
Connecting to the network
Gas discharge light sources cannot be connected directly to the mains. This is due to the fact that in the off state the lamp has increased resistance, so a high voltage pulse is needed for ignition. After the appearance of a charge, a negative differential resistance appears in the light bulb, which requires the inclusion of an additional resistor in the circuit. Otherwise, the light source will break.
Ballasts are used to solve these problems. The most common are two types - electromagnetic ballasts EMPRA and electronic ballasts electronic ballasts.
EMPRA

Devices with an electromagnetic ballast are a choke that has a set of inductive resistances. It is connected in parallel with a fluorescent source of a certain power. With the help of a choke, a trigger pulse is formed and the electric current passing through the light bulb is limited. The benefits include:
- high reliability;
- simplicity of design;
- long service life.
Disadvantages:
- startup duration is 1-3 seconds;
- more energy is required compared to electronic ballasts;
- buzzing;
- flickering;
- large sizes;
- does not work at negative temperatures.
The wiring diagram uses a starter, which is a neon lamp connected in parallel with a capacitor. The starter has 2 electrodes - rigid fixed and bimetallic, which bends when heated. The electrodes are normally open; they close when an electric current is applied.
A small capacitor is connected in parallel to create a resonant circuit. This helps to form a long pulse to light the bulb.
Electronic ballast

The electronic ballast is distinguished by the absence of a flashing light. It supplies the light source with high-frequency voltages up to 133 kHz. There are 2 types of electronic ballasts according to the starting method:
- cold - the lamp glows immediately after switching on, suitable for lamps that are rarely used;
- hot start - the electrodes warm up, the lamp lights up after 0.5 - 1 sec.
Benefits:
- quick start;
- energy consumption is 20-25% lower;
- less material costs for disposal;
- availability of devices with a dimmer on sale.
Compared to lamps using an electromechanical ballast, a starter is not required for the operation of the electronic ballast. The ballast can independently generate the required stress sequence. There are different ways to start lamps. Heating of cathodes with a voltage of a higher frequency than the mains one is usually used.
The components in the circuit are selected so that electrical resonance occurs in the absence of charge. It leads to an increase in the voltage between the cathodes. This makes the light bulb easier to ignite.
Major malfunctions

The main reasons why fluorescent fluorescent lamps fail include:
- Tungsten filament wear. Electrodes are made from a tungsten filament, which is covered with an active mass. Over time, the coating breaks down and crumbles, causing the filament to fail.
- Constant operation of the starter in bulbs with electronic ballasts. It is directly related to the burnout of the electrodes. With the constant operation of the starters, the lamp starts blinking, which negatively affects human health.
- Throttle malfunction. If the choke breaks down, the electric current in the circuit increases significantly, which causes the electrodes to heat up sharply. High temperatures destroy the electrodes and the lamp stops working.
- Poor protection in lamps with electronic ballasts. In devices with electronic ballast, an automatic shutdown circuit is installed when the lamp burns out. In cheap devices from an unknown manufacturer, protection may be of poor quality or be absent altogether. This leads to an increase in voltage and burnout of the ballast transistors.
- Wrong capacitor selection. If the capacitor does not fit the lamp power, a breakdown will occur.
If the lamp is broken, it is difficult to repair it yourself. It is recommended to contact a specialist or purchase a new device.
Fluorescent lamp marking
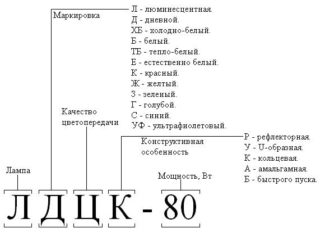
There are 2 types of markings for fluorescent lamps - domestic and foreign.
Domestic marking is written in alphanumeric form:
- The first letter, L, stands for "lamp".
- The second characterizes the luminous flux (D - daytime, HB - cold white, TB - warm white, EB - natural white, B - white, UV - ultraviolet, R - red, H - green, D - blue, C - blue, F - yellow).
- The third letter is the color quality. Sometimes Ts - improved quality and TsTS - especially high color rendering.
- The fourth letter is construction. A - amalgam, K - ring, U - U-shaped, B - quick start, R - reflective.
- The number indicates the power of the lamp in watts.
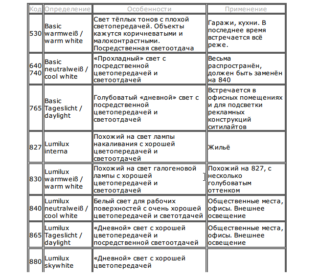
Also, natural white can be marked with the symbols LE - natural and LHE - cold natural.
Special-purpose lamps also have their own markings.The letters LN, LK, LZ, LZh, LR, LGR, LUF are marked with colored lamps.
Foreign labeling uses a three-digit code and signature in English. The color rendering index (the first digit in the format 1x10 Ra) and the color temperature (the last 2 digits) are recorded in digital form. Sources with marking 830, 840, 930 are used in houses.
Recycling light bulbs
The hazardous substances that make up the lamp require special disposal of the device after failure. It is forbidden to dispose of lamps together with household waste - this can lead to a deterioration of the ecological environment.
In order to properly dispose of the devices, special collection points have been established. They are in the management companies of the region, it is prescribed by law. You can return a light bulb for free.








