Soils in the places of construction of various buildings, construction parameters sometimes determine increased requirements for the properties of the bases. The foundation on reinforced concrete piles is distinguished by reliability, durability and high bearing capacity. Piles are of different designs; they are made from different materials suitable for the conditions of future operation. Before installation, it is necessary to evaluate all the pros and cons.
What is a pile foundation
The foundation consists of several deeply grounded piles, interconnected by a grillage, on which the walls are built.
The procedure for the design and arrangement of this type of foundations is determined by the Code of Rules of the joint venture 24.13330.2011.
The main purpose of the driven products is to cut through soft surface soils and transfer the mass of the structure to the underlying dense soils.
Scope of application
Reinforced concrete products are used in private and industrial housing construction.
Cases in which it is preferable to arrange a pile foundation:
- areas with surface groundwater;
- soils with weak bearing characteristics;
- terrain with deep freezing of the earth, permafrost conditions;
- buildings of large mass, when it is necessary to redistribute the load on all sides of the foundation;
- steep slopes.
Sandy, sandy loam, loamy soils and peat bogs are suitable for arranging such foundations. Here there is a high probability of horizontal displacements with fluctuations in climatic conditions - temperature and humidity.
Advantages and disadvantages of technology
- One pile, depending on the section and soil, can take a load from 8 to 60 tons. Such a foundation, even with a shallow grillage, is enough to withstand the mass of a three-story brick house.
- Concrete does not disintegrate in the soil; houses can serve for over 100 years.
- Pile foundations do not lend themselves to displacement in the horizontal and vertical plane, which is important on heaving soils.
- The length of the structure allows it to pass a layer of peat bog up to 30 m deep and support the structure on solid ground.
- The completion speed for a private house takes no more than 2 days.
- Low foundation cost for light soils.
The disadvantages of reinforced concrete piles are associated with the installation features:
- it is necessary to take into account the shock loads on nearby houses;
- the impossibility of erection in cramped conditions, since significant space will be required for driving equipment and the supply of building materials.
On solid soils, the cost of pile foundations exceeds the cost of arranging tape-type foundations.
Types and labeling of products

When deciding to use concrete piles for the foundation, it is necessary to study their characteristics, know the designation according to GOST, in order to order and purchase the necessary building materials.
The types, markings and parameters of products are determined by GOST 19804-2012.
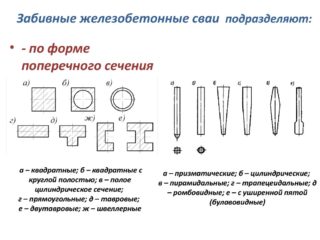
By the method of installation, piles are distinguished:
- submerged by hammering;
- vibro-submersible;
- crushed;
- boring;
- drilling runners;
- downward.
In some cases, the immersion methods are combined, then the assigned name speaks of the main installation method. For example, first, a hole is dug for installation in a vertical position, and then the structure is driven to its full length.
Foundation reinforced concrete piles are marked in accordance with the requirements of GOST 23009.The designation contains several groups separated by hyphens.
- Group No. 1 reveals the type of product, the length measured in decimeters, and the dimensions of the sides of the cross-section in cm, for round products - the diameter.
- Group 2 contains information about the steel class of prestressing reinforcement or drawing number for products with non-prestressing reinforcement - this information is important for designers.
- Group No. 3 contains information on design features, for example, on completing with a steel tip (letter n), type of docking for prefabricated products. "C" - glass joint, "SV" - welded, "B" - bolted.
Additional symbols may indicate characteristics not specified in the first groups.
Examples of alphanumeric designations:
- C60.35-A800. C-type product. Length 6 m, side size 350 mm, reinforcing steel of class A800.
- SO140.100-3-b. CO-type, total length 14 m, diameter 1000 mm, reinforcement option No. 3, bolted joints.
The piles are of different sizes and shapes.
Shapes and main dimensions of standard products
- C - solid with a round or square section, internal non-tensioned reinforcement. The composite version is made with transverse barrel reinforcement. Section (radius) 200 mm, length 3–6 meters.
- C - with prestressed reinforcement, one-piece. The length depends on the cross-section (section / length): 200 / from 3 to 6 m, 250 mm / 4.5–6 m, 300 mm / 3–15 m, 350 mm / 8–20 m, 400 mm / 13–20 m.
- C - composite with prestressing reinforcement, diameter 300, 350 or 400 mm, total length from 3 to 28 meters.
- SP - square section, circular cavity inside, diameter 300 or 400 mm, length 3–12 m.
- SK - one-piece or composite product with tension-free reinforcement, diameter 400–1600 mm, length 4–18 m.
- CO - shell piles, solid or composite, with a diameter of 400–1600 mm, with a total length of up to 24 m.
- 1SD - columns with a square cross-section without cavities with two consoles. Placed on the extreme sides of buildings. Section 200, 300 mm, length 5–7.5 m.
- 2SD - similar in size, but designed for the middle axes of buildings without internal load-bearing walls.
- SC - solid, one-piece with prestressing reinforcement in the center of the barrel. The section is square.
Composite types must be supplied complete with connecting elements provided for in the technical documentation.
Appendices A.1 and A.2 of GOST 19804-2012 contain complete information about which type is suitable for the foundation, depending on the surface and underlying soils.
Installation sequence

The foundation on driven piles is erected according to the technology common to all types of foundations. Sequence of work:
- Conducting geotechnical surveys to determine the composition and characteristics of the soil at the construction site. Including the possible harm to neighboring buildings is being studied - the destruction of buildings can occur from impacts during hammering.
- Coordination of earthworks with organizations that may have underground communications in the area of work (water and gas pipelines, electrical cables, communication cables, sewage networks).
- Drawing up a project, determining the appropriate type of piles. It is important to take into account the availability of free specialized equipment that works with a specific type of submerged products.
- Site preparation for work - cleaning of vegetation, debris, leveling the surface.
- Organization of access roads for special equipment and delivery of components.
- Drainage of groundwater and drainage of the site, if necessary.
- Digging a pit.
- Organization of power supply to the construction site for lighting the place of work and power supply of special equipment.
- Site marking with the definition of the exact location of the piles.
- Directly installing underground foundation parts.
The installation method depends on the availability of special equipment from the contractor.
Driven piles for a private house are distinguished by increased bearing capacity. The effect is achieved due to the fact that when hammering, the soil around the product is compacted and the load from the walls is distributed over its entire surface.
A special machine grabs the element, gives it a vertical position and gradually hammers the reinforced concrete structure into the ground with hammers weighing from 1.5 to 9 tons. In most cases, this method is the fastest.
Reinforced concrete piles for the foundation can be immersed in other ways:
- vibration with pressure;
- indentation;
- by lowering it into a pre-dug well.
Whichever installation method is chosen, the result is always a durable foundation that can withstand increased loads. In some cases, you cannot do without reason. The appearance in construction organizations of reliable special equipment makes pile reinforced concrete foundations popular in the construction of private houses.









good article for beginners