The construction of any residential, commercial and administrative building begins with the arrangement of its foundation. The comfort of staying in the premises and the duration of operation of the building itself depend on the quality and applied technology of manufacturing such structures. Fixed formwork for the foundation is a technological solution that allows you to solve several engineering problems at once without increasing the inevitable costs. There are several options for the manufacture of such structures.
Features of permanent formwork

In its essence and definition, a permanent formwork is a form in which a reinforcing cage is laid and a cement mortar is poured. The difference from the technology of removing the form after the concrete has hardened is that the material for its manufacture remains in place. The purpose of such actions is the absence of dismantling works and the creation of a technological protective layer between the foundation and the ground.
Features of such designs:
- Strength. This quality allows the structure to maintain its configuration and integrity under the pressure of the concrete solution from the inside, and the soil from the outside.
- Tightness. The material should not absorb moisture and have gaps. Otherwise, the composition of the solution will be disturbed, it itself will seep through the seams, which will lead to overspending of the mixture.
- Correctness and clarity of the geometry of the constituent parts. This is necessary to create smooth walls and precise right angles.
- Durability. The material is selected with the longest possible service life, since it affects the bearing capacity and condition of the foundation. Frequent replacements are costly and inconvenient.
Sometimes the expanded polystyrene formwork rises to the entire basement level. In such cases, measures are taken for its additional facing. Coatings are selected that are resistant to mechanical stress, moisture and ultraviolet radiation.
Varieties of material
Modern technology has provided builders with a wide range of materials that can be used in the manufacture of permanent foundation casting molds. Products differ in many respects, have their own advantages and disadvantages. The correct choice can only be made after a comprehensive assessment of each material.
Expanded polystyrene

Boards made of polystyrene are very popular in private construction. The material has been tested for decades and has proven itself well in the construction of residential and industrial facilities.
Expanded polystyrene formwork for the foundation has the following advantages:
- low specific gravity - foam blocks are easy to transport and lay without significant effort;
- the presence of a tongue-and-groove docking system simplifies the installation process and ensures the tightness of the seams;
- high laying speed due to the impressive dimensions of the polystyrene formwork;
- a wide range of products in terms of composition and strength;
- tightness, immunity to dampness;
- excellent heat and sound insulation characteristics;
Penoplex formwork has its drawbacks:
- fragility;
- destruction under the influence of ultraviolet radiation;
- the release of harmful substances into the air;
- flammability;
- limited service life (up to 25-30 years).
Foam formwork is an effective solution for the construction of structures with simple geometry, where there are no rounded surfaces, sharp and obtuse corners.
Arbolit
Arbolite blocks have the following advantages:
- high strength;
- affordable cost;
- durability;
- small specific gravity;
- ease of processing;
- ease of installation and assembly without the use of lifting equipment;
- excellent insulating qualities;
- sturdy surface;
- environmental Safety;
- fire resistance;
- frost resistance.
The only but very significant drawback of the material is its hygroscopicity. It can be used as a formwork only if high-quality waterproofing is carried out, and this is associated with additional time and financial costs.
Glass magnesite

The material has a complex composition containing natural and synthetic elements based on sawdust and fiberglass. Magnesia glass has a beautiful surface and can be used as permanent formwork for the underground part of the building and for the basement.
The panels have the following advantages:
- low specific gravity;
- waterproofness;
- good thermal insulation properties;
- fire resistance;
- ecological cleanliness;
- strength to vertical and horizontal pressure;
- some flexibility, sufficient to create curved surfaces;
- ease of processing with hand tools.
The disadvantage of glass magnesite is its high price. In addition, production is carried out only in China, and this is an additional cost.
Metal sheet profile

Profiled sheet formwork is widely used in private and industrial construction. Products from black iron, stainless steel and aluminum are used. The mold is assembled using rivets, studs and self-tapping screws, depending on the chosen design.
Material advantages:
- relatively low cost;
- strength;
- durability subject to high-quality coating;
- almost absolutely precise geometry of the sheets;
- a wide range of products, differing in profile sizes and finishes.
Cons of corrugated board formwork:
- limited service life due to metal corrosion;
- sharp edges that you can cut yourself;
- the complexity of the assembly;
- the need to spend time and money on sealed joints.
The installation process can be somewhat simplified by using aluminum panels, which are lighter and impervious to moisture.
Decorative model

Decorative blocks available for sale on the construction market are hollow products consisting of two sand-concrete panels, fixed to each other by steel ties. Depending on the model, the decor is applied to one or both sides. The distance between the shields also varies. If necessary, insulation plates are inserted inside. Docking is done in sealed locks on the edges, no additional steps are required.
Advantages of decorative formwork:
- a combination of a form ready for pouring a solution and an external facing;
- a wide variety of shapes and sizes;
- quick and easy assembly;
- the presence of shaped parts (corners, rounding, contours);
- waterproofness;
- ecological cleanliness;
- durability;
- a large selection of styles and colors of decor.
The disadvantage of such products is only in their cost.In private construction, only wealthy people can afford such an acquisition.
Purpose and application
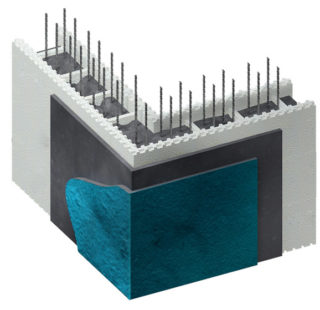
Permanent formwork is widely used in the construction of structures of various purposes and sizes. This structure simultaneously serves as a mold for pouring the solution with its subsequent hardening and isolation of the reinforced concrete foundation from external factors. These include cold, moisture, soil pressure and chemically active reagents in it. It doesn't matter if there is a basement behind the wall or not. The foundation itself needs protection, and the creation of comfortable conditions is a secondary factor in such an engineering solution.
The scope of application of fixed formwork is practically unlimited. It is used in the construction of such facilities:
- private cottages, summer cottages, mansions;
- multi-storey buildings with a deeply buried base;
- garages with inspection pits;
- catering establishments, including those with cellars;
- entertainment establishments;
- administrative and utility buildings;
- pedestrian, road and railway bridges made of reinforced concrete.
The list goes on and on, since this technology is applicable to almost all types of construction. Only the nuances of the choice of material remain, which are determined by a number of factors inherent in each specific project.
Specificity of connecting elements
The issue of joining the formwork elements requires special attention. The degree of its strength and tightness plays an important role at the stage of pouring concrete, after its hardening and backfilling of the soil. When choosing a material, it should be borne in mind that the docking nodes can be made in advance by the manufacturer or they will have to be made independently.
There are such options for connecting formwork fragments:
- Thorn-groove system. Edges are made on plates of expanded polystyrene, wood concrete, glass magnesite and some models of foam concrete. After joining, the seams do not acquire tightness; for this, a sealant is added to the docking unit.
- Overlapping waves. Used when assembling a form from a profiled sheet. As a rule, the overlay is made for one large bend. A sealant or rubber gasket is placed between the sheets, after which the joint is pulled together with hardware, it acquires strength and water resistance.
- Bonding. The technique is used when plywood or smooth steel sheet is used for assembly. Aluminum tape is glued to the joints, providing a reliable, sealed and durable connection.
- On hairpins in shaped grooves. This is how the decorative formwork fragments are connected. The docking assemblies are pre-made and are easy and quick to assemble.
During the construction of various structures, it is allowed to use formwork of different type and type, provided that the same thickness of the supporting structures is maintained.
Do-it-yourself fixed formwork installation

For the installation of permanent formwork made of sheet materials, followed by pouring the mortar, the following tools and materials will be required:
- concrete mixer;
- Bulgarian;
- pliers;
- hacksaw, hammer;
- level, tape measure;
- putty knife;
- sand, cement and crushed stone;
- fittings;
- thin wire or plastic ties;
- marker.
Sequence of work:
- Measurements. Cutting slabs into fragments, which, when assembled, form two planes corresponding to the configuration of the trench and basement.
- Backfilling in the trench. Wetting, leveling and compacting the pad. Pouring a thin layer of cement mortar to the bottom to eliminate possible cracks.
- Installation of slabs on the bottom of the excavation, their alignment vertically and horizontally. Fixing the panels with nails, rods or plastic pins.
- Sealing cracks and joints.Depending on their size, silicone sealant or polyurethane foam is used. After hardening, the excess is cut off.
- Sealing joints with aluminum tape. Previously, the material must be cleaned of dirt and dust, preferably treated with an alcohol solution.
- Knitting and laying of an iron frame. It is better to connect the rods with a wire with a lining of the ends of at least 10 cm. The use of welding causes the development of rust, which can eventually break the concrete.
- Installation of screeds and supports, which will give the formwork strength.
After checking the quality of the operation performed, the concrete is kneaded and poured. In the process of filling the mold, air must be removed from the solution using a steel rod or a deep vibrator. The final step is to level the concrete with a trowel. After that, the foundation is covered with plastic wrap and left alone for 28 days to harden.
Advantages and disadvantages of fixed formwork

The main advantages of the technology:
- ease of manufacture;
- protection from dampness and cold;
- reduction of construction time due to the absence of dismantling and backfilling processes;
- saving money on removable materials;
- applicability to buildings of any configuration and height;
- minimization of the amount of waste.
Disadvantages of the design:
- the complexity of construction at subzero temperatures;
- impossibility of repair and dismantling;
- susceptibility of porous materials to destruction by rodents.
With a competent approach, the use of fixed formwork allows you to save good money on construction with obvious benefits for the final result.