When planning construction, special attention is paid to the choice of the type and size of the building base. Up to 40% of the estimate is spent on such structures; not only the durability of the house, but also the very fact of its existence in the foreseeable future depends on their reliability. One of the options for arranging the support of the structure is a columnar foundation. The design of this type has its own characteristics, pros and cons, construction and operation rules. Before making a final decision in favor of a pillar foundation, you should familiarize yourself with the technology of its construction and the types of materials used.
Features and design of a columnar foundation

This type of foundation is a collection of supports installed in the ground according to a certain pattern. The type, number and size of pillars depends on a number of factors, the main of which are the composition of the soil and the weight of the building. Since the area of the supports is much smaller than that of a strip and slab foundation, their bearing capacity is proportionally lower.
Single supports can be used in the construction of light frame-type country houses, structures made of foam blocks and sandwich panels. For heavy houses, a larger number of pillars are made, which, together with the mandatory installation of a grillage, makes such a decision impractical. It is easier, faster and more reliable to pour a reinforced concrete structure.
When deciding to make a foundation on pillars, one should take into account the following features of this structure:
- The base of the pillars must rest on a solid layer of soil. You need to be prepared for a passage of rather deep holes.
- The base device can be single or one-piece. In the first case, the supports are rigidly united by a grillage, in the second, a floor slab or lower fragments of a beam is lowered onto them.
- The clearance under the house is chosen sufficient to provide ventilation, protection from cold and dampness. The opening can be used for storing various small items. The minimum allowable elevation is 50 cm.
- When assembling supports from small fragments, a high-quality binder is used.
A columnar foundation is rarely used as a permanent base. Basically it is made for temporary huts, light and collapsible buildings.
Varieties by material
In private construction, the following projects can be implemented:
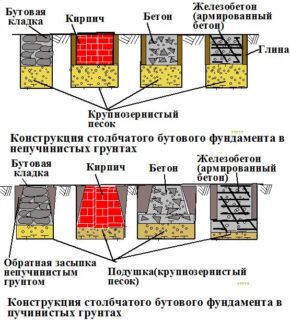
- Columnar monolithic foundation. It is a single reinforced concrete structure consisting of rods lowered into the ground, connected at the top with a continuous tape. A waterproof mixture is used for the lower part of the structure, while a cheaper one can be used for the upper one.
- Brick foundation. It is considered to be the easiest technology to implement, which does not require large expenditures and the involvement of heavy equipment. Only fired clay bricks are used. In addition, you need a reliable and stable base.
- Blocky. Blocks of various sizes are used, from the smallest to standard FBS. It is better to choose blocks that are connected in spikes and grooves.This design excludes their mutual displacement under the influence of vertical loads.
- Foam concrete. This type of foundation has sufficient strength, but cannot be installed on unstable soils and on slopes. Strength is achieved by adhesion of the edges of stones, clay bricks and ceramic fragments, fixed with cement mortar.
- Wood. Wooden supports are rarely used due to their limited strength and fragility. To extend the service life, the material is treated with an antiseptic, impregnated with linseed oil, creosote or other water-repellent agents. Before lowering into the well, the log is additionally lubricated with bitumen and wrapped in roofing material.
- Asbestos pipes. The pipes themselves perform the functions of formwork and waterproofing. After installation and alignment of the pipe in the hole, reinforcement and grouting is carried out. Fragments protruding from the ground are periodically cleaned of dirt and rot, then painted.
- Metal piles. Screw products are used on soft ground, when stable layers occur at a considerable depth. Screwing in is carried out manually or mechanically. After installation, the excess metal is cut off, a concrete solution is poured into the cavity, and the head is welded.
In the construction of buildings, supports of various types and sizes can be used. The choice is made after conducting a study of the soil and calculating the expected loads by points.
Varieties according to the degree of depth
According to the degree of burial in the ground, columnar foundations are divided into the following categories:
- Shallow. They fall to a level of 30-50% of the freezing point of the soil. They are used in dense soils and on stony surfaces with a minimum coefficient of heaving of the earth during freezing.
- Shallow. They deepen to 70% of the freezing level. They are used on soils, the degree of heaving of which does not exceed 3%.
- Recessed. Set up on wet and unstable soils at a depth greater than the freezing level.
Geological surveys may be required to determine the type of soil. Data on the level of freezing can be obtained from local authorities and accounting.
Calculation of a columnar foundation
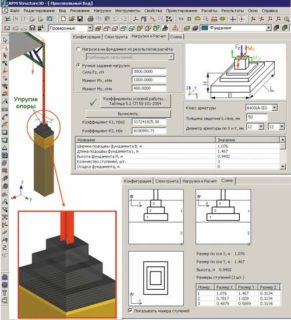
A competently carried out calculation of the foundation will allow the construction of a structure of sufficient strength, without spending extra money on achieving reliability, which simply will not be in demand. Initially, it must be borne in mind that the support block is not designed to accommodate heavy reinforced concrete slabs and thick brickwork on it.
The drawing of the future structure must contain the following data:
- support arrangement diagram;
- material for making rods;
- pile immersion depth;
- applied technology.
When designing, you cannot rely on luck or building experience from your neighbors. Achieving the desired result is possible provided that all related factors are taken into account and the available information is used wisely.
The initial data for the calculation include:
- soil structure;
- depth of groundwater;
- bearing capacity of the soil;
- the level of freezing of the earth;
- maximum and minimum snow depth;
- material strength;
- the weight of the building with furniture, household appliances and communication systems in it.
Information on the bearing capacity of the soil can be obtained from the tables of the SNiP 2.02.01-83 document. The weight of the building is calculated using simple mathematical operations. You can get data on supporting structures by multiplying their volume by the density, which is indicated in the instructions for the product.
In the future, you need to divide the mass of the structure by the soil resistance indicator and multiply by 1.5 in order to have a margin of safety.The result will be the area that the bases of the posts should create on the ground. It remains only to divide this number by the section of one pillar and get the number of required products.
The final stage of the calculations is to determine the location of the supports, here the principle of uniformity must be observed and the distance between them must not exceed 200 cm to prevent sagging of the connecting beams.
Preparatory work

The technology of preparing for arranging columnar bases is not particularly complex, but must be performed correctly.
Step-by-step process of the initial stage:
- Determination of the construction site in accordance with the project. Marking it with clearly visible landmarks.
- Removing bushes, grass, trees, debris and other foreign objects from the site.
- Marking. First, the outline of the building is indicated, then the points of installation of the supports.
- Checking the horizontal position of the site It is not necessary to align it, since this can be done during installation by varying the height of the posts.
- Removal of the top layer of soil in an area exceeding the parameters of the building by 200 cm on each side.
- Laying on the surface of a geotextile fabric to prevent the germination of grass and shrubs. Covering the canvas with a layer of rubble.
- Excerpt of pits to the design depth. Sealing their bottom.
The final phase of preparation for construction is the arrangement of sand and fine gravel cushions in the holes. The filling height can be 20-40 cm.
Installation rules

In order to build a high-quality columnar foundation with your own hands, you should adhere to a number of rules that are determined by regulatory documents.
- The foundations for light extensions to the main building should be made separate. The weight of the structures is different, therefore the shrinkage is different, lower costs for additional structures are required.
- When pouring concrete into boreholes, steel or plastic pipes, a metal frame must be used. This part significantly strengthens the support and makes it more durable.
- The pillars must be laid at the corners of the building, under the load-bearing walls, as well as under the interior partitions, doors and windows.
- After installation, the pile heads are aligned at one level.
Installation of the grillage allows you to make the foundation more resistant to vertical and horizontal loads. This structure can be monolithic or prefabricated, usually used to support heavy houses.
Pros and cons
Like any engineering structure, columnar foundations have their pros and cons.
Design advantages:
- minimum labor costs;
- the ability to do it yourself;
- small cash investments;
- simplicity of technology;
- speed of construction;
- a large selection of materials.
Disadvantages of structures:
- restrictions on the type of soil and relief;
- small bearing load;
- the likelihood of breakage of brick and wood products.
The technology is the optimal choice for carrying out the construction of lightweight buildings on a limited budget.