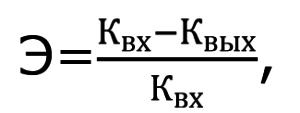The fundamental difference between industrial ventilation is that the equipment can cope with the maintenance of large rooms, often with very difficult microclimate conditions. Harmful substances, hot steam or dust can be released into the air. The main task of the exhaust ventilation of industrial premises is to quickly "catch" all unwanted impurities and remove them without harming the environment.
- Types of room ventilation
- Natural ventilation in industrial buildings
- Indoor air aeration
- Natural ventilation device in production
- Forced ventilation in industrial premises
- Types of industrial air inlets
- Types of industrial fans
- Dust collectors and filters for work in production
- Supply ventilation in production
- Local supply system in the room
Types of room ventilation

According to the air movement method, there are two types of ventilation:
- mechanical;
- natural.
According to the principle of operation, all ventilation units are divided into:
- Supply air (for supplying fresh air), can be local (oasis, curtain or air shower), as well as general (directed or dispersed inflow).
- Fume hoods (exhaust air is evacuated), are general or local.
Natural ventilation in industrial buildings
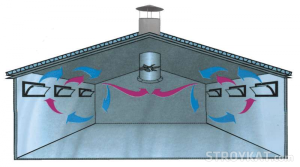
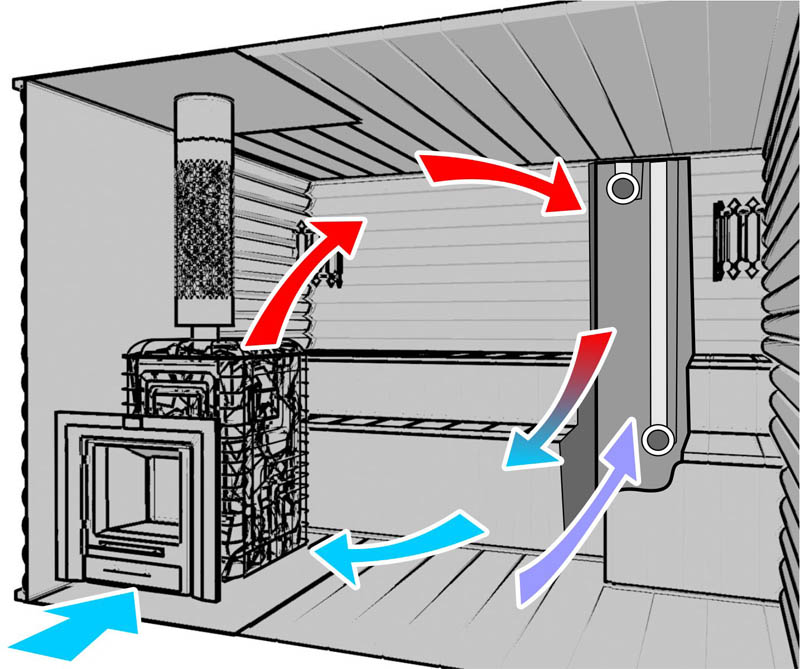
Any natural supply or exhaust ventilation of a production facility operates using the difference in temperature and air pressure in the workshop and outside. This means that the driving force of natural traction is wind and heat head.
Due to the temperature difference, expanded warm air masses are displaced from the workshop, and clean, cold air masses are pulled in their place. An area of increased pressure is formed from the windward region, increasing the flow of fresh air from the outside. On the leeward side of the building, on the contrary, the pressure is always reduced, which facilitates the outflow of exhaust air. Physical laws are successfully used for ventilation of enterprises with intense heat generation. But not in all cases a powerful exchange of air guarantees the creation of all the necessary conditions for the work of personnel.
The more noticeable the temperature difference near the floor and near the ceiling of the workshop, as well as the higher the room, the more efficiently the system will work.
If there are cracks in the walls and windows of the workshop, doors or gates are often opened, drafts and a drop in temperature are likely. In summer, in areas remote from doors and windows, the ventilation standards of industrial premises are violated.
Indoor air aeration
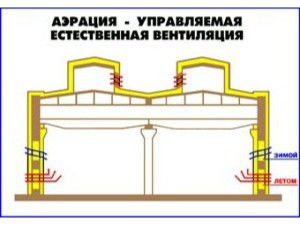
Aeration in some cases creates effective air exchange based on natural draft. For its implementation, aeration lanterns are installed - specially designed ventilation elements.
Sometimes, during the construction of a production facility, ventilation is not calculated, the equipment is not installed. Then it is possible to place mines and canals in the already finished workshop, operating due to the thermal pressure. The exits of the mines are covered with deflector heads. The wind blows over the deflector and forms a vacuum area in the pipe, increasing the suction of air. A similar system is widely used in agricultural and livestock buildings, blacksmiths, small bakeries. The pipe is installed on the highest ledge of the roof.
Aeration is one of the most effective examples of natural industrial ventilation.It is used in industries with abundant formation of gases, poisons and heat.
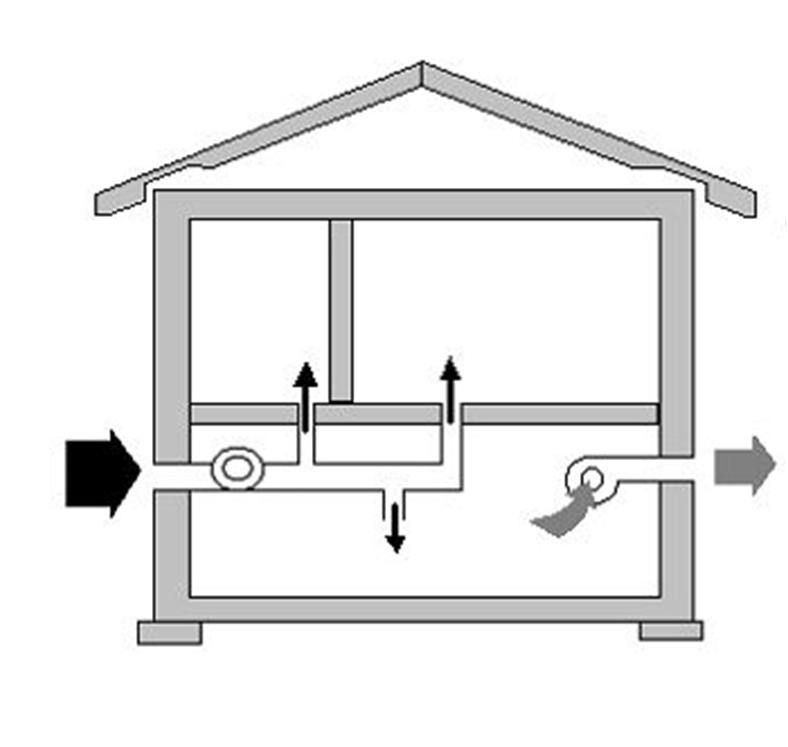
Natural ventilation device in production
The serviced buildings are equipped with 3 levels of openings with specially designed air vents. The first two rows of openings are located at a height of 1-4 meters from the floor. Light-aeration lights with adjustable vents are installed in the roof.
In summer, streams of clean air enter through the lower transoms, and dirty air goes up. In the cold season, air penetrates through the middle row of vents and, warming up, reaches the level of staff availability.
The ventilation intensity is regulated by different positions of the vents. Calculating the ventilation of the production room, determine the area of the vents, openings. Since the worst time for the system to work is warm calm weather, it is taken as a starting point.
In windy weather, natural draft works better. But with a combination of a certain force and direction of the wind, reverse thrust can be created.
Clean air mixed with dust and gases is directed to the areas where people are located. In order to prevent the spread of dust and dirt, lanterns of a non-blowing design with protection from the wind are installed.
In the hot season, the supply air is cooled by spraying cold water into it from the nozzles located in the area of the vents. The air cools down and the humidity increases slightly.
There are some requirements for buildings with natural aeration:
- its perimeter should be open to air access;
- single-storey workshops or high-rise buildings located on the last floors are aerated.
It is very difficult to install natural ventilation in multi-span industrial premises. With a workshop width of more than 100 meters, delivering clean air to the center of the building is practically impossible. Then, for aeration, non-inflated Baturin lanterns with a separate channel for exhaust and inflow are installed. In winter, such a system can cause an undesirable drop in temperature in the working area of the production area. Therefore, in multi-span workshops, forced ventilation with heating of the inflow is usually installed.
All aeration elements are controlled mechanically.
The advantage of this type of ventilation in industrial premises is the ability to provide powerful air exchange.
Another plus is the low cost of the mechanisms.
Disadvantages:
- dependence on the weather;
- complexity of management;
- the impossibility of providing remote workplaces with fresh air.
Aeration, as a type of ventilation in industrial premises, is unacceptable if the technology involves the spread of harmful impurities, dust. Because filtration of waste air masses is impossible.
Forced ventilation in industrial premises

Supply or exhaust ventilation schemes for industrial premises on a mechanical traction make it possible to bring the parameters of the air supplied to the room to the required ones (humidify, filter, cool, heat and render the air harmless).
Benefits of forced ventilation:
- her work is not related to the outside temperature;
- supply, remove air from the required point;
- it is possible to change the ventilation rate of the production room within any limits;
- you can make an accurate calculation of the exhaust or supply ventilation of the production room.
Among the types of ventilation in industrial premises used today, forced draft is the most widely used.
Ventilation in production areas limits the spread of dirty air and removes it directly from the source.
The quality of work of the local ventilation of the industrial premises is influenced by the correct selection of equipment, the shape of the air inlets, and the degree of rarefaction of the atmosphere.
All types of exhaust units for ventilation of industrial premises consist of such components as:
- suction (air intake);
- fan;
- air ducts;
- filters;
- exhaust duct.
The entire volume of dirty air must be captured by the air inlet and then transferred through the local ventilation system of the production area.
Types of industrial air inlets

There are two types of suction or air inlets for ventilation systems:
- closed;
- open.
Open-type ventilation air inlets consist of:
- protective casing;
- exhaust umbrella;
- onboard or articulated telescopic suction (installed directly at the workplace);
- movable air inlets.
Such receivers differ in that the opening for the entry of dirty air is located a little further from the place of its discharge.
The protective dust cover eliminates the dust column (the so-called dust torch), which is formed, for example, in the carpentry industry: during grinding, polishing, on grinding machines. The device contains a visor and is installed across the movement of dust particles.
The multiplicity of local ventilation in the production area is calculated based on the speed and diameter of the grinding or grinding wheel.
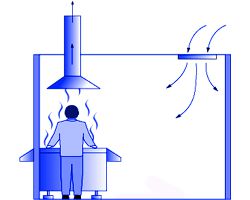
Exhaust hoods reduce the spreading area and remove hot air containing hazardous impurities and rising up according to the convection principle. The size of the umbrella must completely cover the area of the hot air source. Umbrellas are made with or without overhangs. Overhangs are made of rigid sheets or dense canvas. Open umbrellas are more convenient as the overhangs do not interfere with staff access.
In hazardous industries, the speed of the air flow entering the umbrella should be from 0.5 meters per second and higher. If the umbrella removes hot air without impurities, the speed should be between 0.15 and 0.25 meters per second.
Air inlets in the form of slots or onboard suction units are installed on pickling and galvanic baths. The air moves over the bathtub and draws out harmful vapors of alkalis and acids before they spread throughout the room.
If the width of the bathroom is small (up to 70 cm), single-sided suction units are installed.
Wide baths are equipped with double-sided suction systems, as well as structures that blow off evaporation from the surface of the liquid, "with blowing".
The volume of air passed through such devices depends on the surface area of the liquid, the degree of toxicity of the vapors, and the temperature of the liquid. Since vapors quickly destroy metal structures, the ventilation of industrial premises in this direction is made of resistant materials, such as PVC.
In welding and brazing workshops, the suction units are installed on vertical or beveled panels with multiple holes.
Telescopic and articulated suction units are very common. Thanks to the retractable tube, the suction end can be brought closer to the desired location.
In workshops with semi-automatic welding machines and soldering irons operating in carbon dioxide, the suction units are mounted directly into the tools. Such equipment is effective at air exchange up to 20 cubic meters per hour.
If the place of work of the welder is not fixed, mobile suction units are used, some of them on suction cups are attached to the welding machine.
Closed type suction:
- fume hoods;
- cabins;
- shelter boxes;
- cameras.
Fume hoods are installed in workshops with abundant emission of toxic vapors and gases.
Shelter boxes do not provide for open openings and are used in industries with radioactive and highly toxic substances. The worker performs all manipulations by means of rubber gloves and built-in sleeves or mechanical devices.
Local exhaust ventilation in industrial areas with complete isolation of sources of hazardous emissions is called aspiration and is considered one of the safest and most effective schemes.
Types of industrial fans

Air in forced ventilation systems is driven by mechanical devices: blowers powered by electricity. Most often, radial or axial models are installed.
A radial or centrifugal fan is also called a "volute" in the shape of a housing, into which a wheel with blades is built. During the spinning of the wheel, air enters the housing, changes direction and is fed into the air duct under pressure.
The exhaust air is often saturated with harmful and aggressive components and even explosives. Fans are used depending on possible impurities:
- standard type for air with temperatures up to +80 degrees with a small amount of dust;
- anti-corrosion type - for vapors of alkalis and acids;
- spark-proof - for explosive air mixtures;
- dust - used if the dust in the air is more than 100 milligrams per cubic meter.
The fan numbers indicate the wheel diameter expressed in decimetres.
Axial fans are inclined blades installed in a cylindrical casing. During operation, the air moves parallel to the fan axis. Such models are more often installed in medium-sized networks, emergency exhaust ducts and in mines. Their advantage is that one fan can supply air in two opposite directions, carrying out both exhaust and supply.
Air is supplied to the required points through the ducts. Most often they are made from sheet metal, and when working with aggressive substances - from plastic, ceramics and other resistant materials.
Dust collectors and filters for work in production
The quality of air emissions into the atmosphere is regulated by the requirements for ventilation of industrial premises. Therefore, dirty air from industrial plants must be filtered before being released into the environment. One of the most important parameters calculated for the ventilation of a production facility is the efficiency of air purification.
It is calculated like this:
Where KvkhIs the concentration of impurities in the air before the filter, Kvyh- concentration after the filter.
Sometimes a single dust collector or filter cleans the air enough, then the cleaning is called one-stage. If the air is very polluted, it is necessary to organize a multi-stage cleaning.
The type of cleaning system depends on the amount of impurities, chemical composition and shape.
The simplest design of dust collectors is dust settling chambers. The speed of the air flow sharply decreases in them and due to this, mechanical impurities settle. This type of cleaning is only suitable for primary cleaning and is not very effective.
Dust settling chambers are:
- simple;
- labyrinth;
- with a bump stop.
To capture dust with particles larger than 10 microns, cyclones are used - inertial dust catchers.
Cyclone Is a cylindrical metal container, tapering at the bottom. Air is supplied from above, dust particles under the influence of centrifugal forces hit the walls and fall down. Clean air is discharged through a special pipe.
Two small cyclones installed one behind the other increase cleaning efficiency by 90% compared to one large cyclone.
To further increase the amount of dust retained, water is sprayed into the cyclone body. Such devices are called cyclone washers. The dust is washed off with water and sent to sedimentation tanks.
The modern type of dust collectors is rotary or rotoclones. Their work is based on a combination of Coriolis and centrifugal forces. The design of the rotoclones is reminiscent of a centrifugal fan.
Electrostatic precipitators Is another way to remove dust from the air.The positively charged dust particles are attracted to the negatively charged electrodes. A high voltage is passed through the filter. To clean the electrodes from dust, they are automatically shaken from time to time. Dust gets into storage.
Water-wetted gravel and coke filters are also used.
Medium and fine filters are made of filter material: felt, synthetic nonwovens, fine mesh, porous fabrics. They catch the smallest particles of oils, dust, but they clog up quickly enough and require replacement or cleaning.
If the air needs to be cleaned of highly corrosive, explosive substances or gases, ejection systems are used.
The ejector consists of four chambers: discharge, confuser, neck, diffuser. Air enters them under high pressure, carried away by a powerful fan or compressor. In the diffuser, dynamic pressure is converted into static pressure, after which the air mass is carried outward.
Supply ventilation in production

Ventilation standards for industrial premises are specified in SNiP 41-01-2003. Before being supplied to the room, the air should be processed: cooled or warmed, filtered from dust, and sometimes its humidity should be increased.
Supply ventilation device:
- air intake;
- air ducts;
- filters;
- heaters;
- fan;
- air distributors.
When installing the ventilation of the production room, a supply chamber is organized to accommodate the heater, filter and fan.
Air inlets are located at a height of 2 m above ground level, in places far from sources of pollution, sometimes above the roof of a building. When choosing a place, the direction of the winds is taken into account. Outside, the air intakes are covered with blinds, grilles or umbrellas.
The supply air is cleaned by filters of various types, usually of non-woven materials.
The air is heated in winter with shades or heaters. The heat carrier is water or electricity. If humidification is necessary, irrigation chambers are installed, where a finely dispersed fraction of air is sprayed. Air is cooled in the same way.
Local supply system in the room
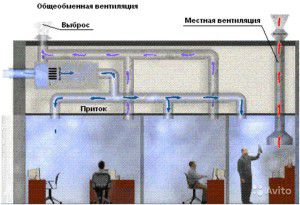
Ventilation requirements for industrial premises are not always met by general ventilation. And then the local supply system is installed.
Types of local supply ventilation:
- air-thermal curtains;
- air showers;
- oases;
- air curtains.
Air shower it is a stream of clean air directed to the workplace. Its purpose is to enhance the heat transfer of the employee's body and prevent overheating.
Shower installations can be:
- stationary;
- mobile.
Dusking is organized in hot shops, as well as with infrared irradiation of personnel over 350 W / sq. meter.
Ventilation rates for industrial premises of this type depend on the severity of the work, the air temperature in the workshop and the intensity of infrared radiation. On average, the air temperature in an air shower is from +18 to +24 degrees. The stream moves at a speed of 0.5 to 3.5 meters per second. The speed is directly proportional to the air temperature and the intensity of the irradiation. And the supply flow temperature is inversely proportional to these indicators.
To change the direction of the air flow, special rotating nozzles are attached to the ends of the air ducts.
Air oases serve the entire section of the workshop, which is fenced off from the rest of the area by light screens. In the area, air moves at a calculated speed and temperature. In an oasis, the ventilation rate of an industrial building is carefully calculated.
Air-thermal and air curtains are designed to prevent overcooling of employees and cool the premises through open doors or openings.
There are 2 types of curtains:
- with heated supply air;
- without heating.
General exchange ventilation is necessary in cases where moisture, heat and pollution enter the entire volume of the workshop and it is impossible to comply with the ventilation standards of production premises with the help of local measures. With a general ventilation system, the exhaust air in the production room is diluted with clean air to meet the requirements of sanitary and hygienic control. It is not a frugal or very efficient system.
To prevent the suction of dirty air from the workshop, ventilation chambers and air ducts are carefully sealed and ventilation of the production room is installed in the cleanest places.
According to the standards of sanitary and hygienic control of ventilation systems of industrial premises, all components are kept clean and undergo periodic checks.
Air is supplied at a speed of up to 15 meters per second through slotted air ducts, creating a barrier to the flow of cold outdoor air. More about air curtains in the video: