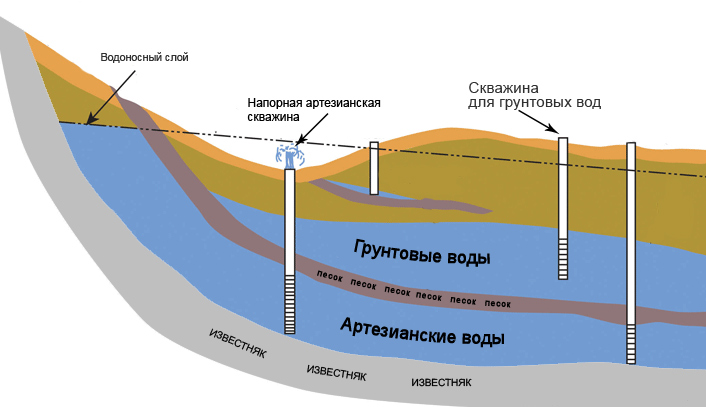
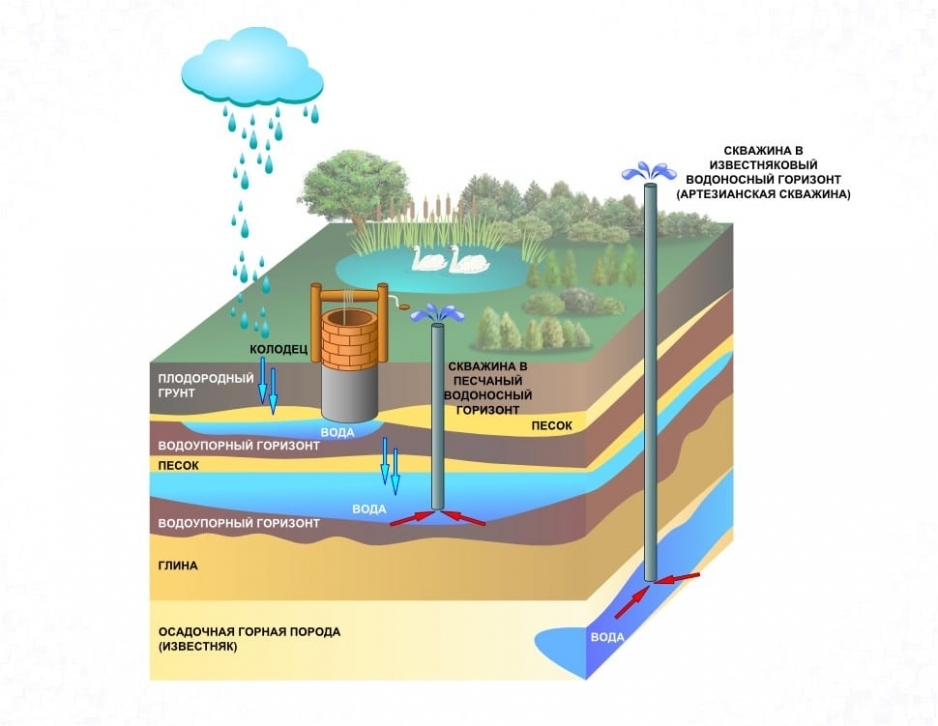
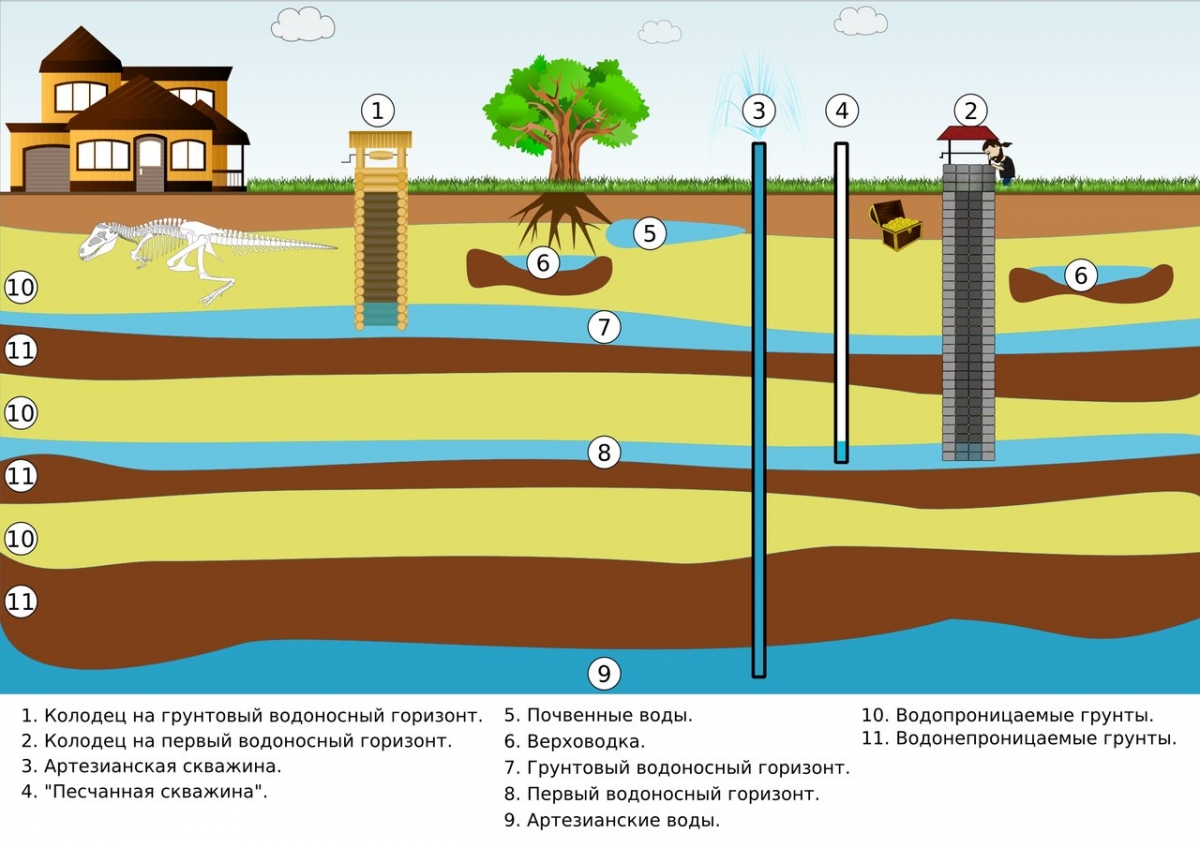
Well water in a country house or suburban area is one of the cleanest. However, there are frequent cases of its increased mineralization or enrichment with manganese and iron. It is not recommended to drink such liquid without preliminary purification. If there is a lot of iron in the water from the well, its use can lead to kidney, liver and even heart attack.
Why are iron impurities in water dangerous?

More often, Fe is in a liquid in a bivalent state - dissolved, invisible to the human eye. Not knowing about the enrichment of water with this element, you can use a supersaturated liquid for a long time, which leads to negative health consequences:
- renal failure;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- liver problems;
- heart pathology;
- allergic skin reactions;
- harmful effect on the nervous system.
Washing with such water is unpleasant, unsafe.
For household appliances, a high concentration of Fe in water is dangerous by the formation of corrosion and plaque. Laundry from washing in such a liquid acquires a yellow tint.
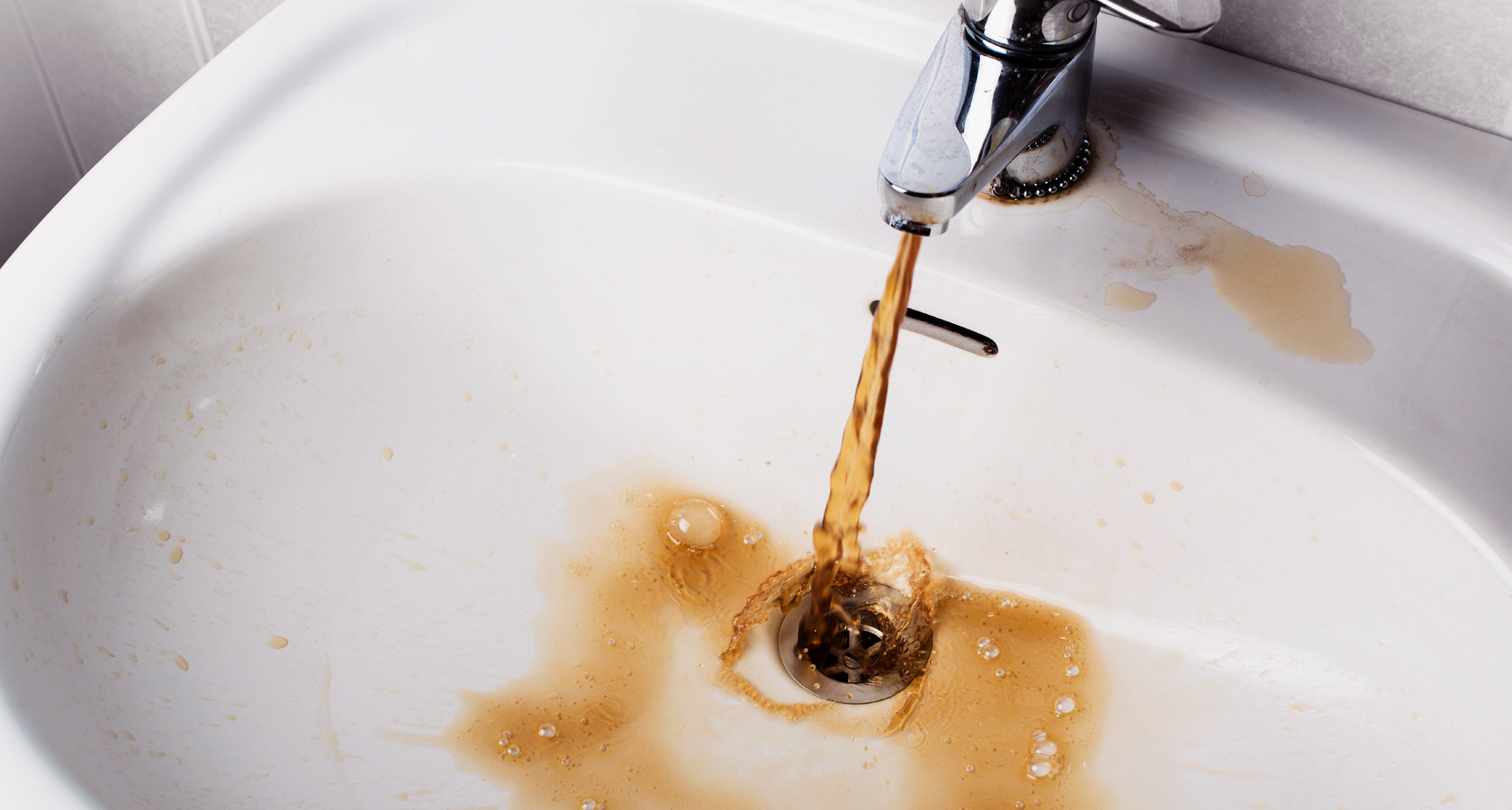
Water saturated with iron takes on a reddish color 2-3 hours after rising. This means that the oxidation process of bivalent Fe has passed. As a result of the combination of oxygen with a chemical element, it transforms into a trivalent form, takes the form of suspensions, which are already distinguishable in water.
Signs of having iron
- Changing the color of the liquid some time after it was selected from the well.
- A layer of red-colored sediment at the bottom of a glass container with water.
- The liquid smells like iron, has a rusty smell.
- Specific metallic taste in fresh borehole water and cooked dishes.
- White laundry turns red after washing.
- Boiling will form a fine-grained, rusty precipitate in the cookware.
It is necessary to remove chemical impurities from the well resource of a private house in a timely manner and correctly, until the problem manifests itself.
The rate of Fe content in water is only 0.3 mg / l. Its large concentration already has a negative effect on the human body.
Methods for deironing water
Upholding
With this method, ferrous iron is oxidized. The method is good for preparing just drinking water. You just need to collect the liquid in a glass container and wait until the sediment in the form of rust settles to the bottom. The top 2/3 of the water is potable. The ineffectiveness of this method is that when overflowing, a certain amount of sediment can get into a clean container.
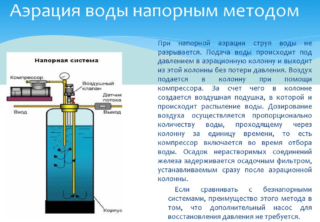
Aeration
- Pressure head. The process involves forcing air by a compressor into a flask filled with water. After the oxidation process has passed, the liquid is fed into filtering installations (coal, mechanical, ion-exchange). The output is a clean resource suitable for consumption.
- Free-flow. The so-called stifling occurs. The liquid is fed into a large reservoir through a spray can (nozzle). On contact with oxygen, the iron in the water is oxidized and precipitated.It remains to remove it through the filters.
The aeration method is considered the most relevant of the household ones after the installation of iron-removing filters.
Ozonation
- In a special installation, atmospheric air is cleaned of all impurities and contaminants.
- It is fed to an oxygen concentrator, where the substance is converted into a gas mixture. The oxygen content in it reaches 90-95%.
- The processed air enters the ozone generator, where the desired substance is formed.
- Water is enriched with ozone as aeration.
Ozonation is used for industrial, large-scale purposes. Household installations are ineffective because they are not able to produce the required amount of ozone for high-quality water purification. This is due to the safety of an ordinary consumer. Ozone is an explosive gas.
Ion exchange installations
Dispose of ion exchange resin with household waste is prohibited. This leads to environmental pollution.
Reverse osmosis
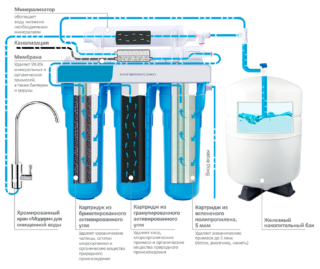
This method of purifying water from iron from a well to drinking water in a country house is the most effective. Reverse osmosis plants are several stages of liquid processing and its additional saturation with minerals, if necessary.
The principle of water purification from iron is simple - a liquid under high pressure passes through a fine-grained membrane, which allows only water molecules to pass through, but not ions of chemical elements, lime, nitrates. All waste is discharged in a salvo into the sewer. This prevents the membrane from clogging, but still requires regular cleaning.
Reverse osmosis systems handle borehole fluids, the concentration of iron in which does not exceed 15 mg / l.
It is recommended to buy a reverse osmosis unit from a trusted supplier and order its turnkey installation with subsequent maintenance.
Filtration

Filters can remove iron from the water from the well if it is in a suspended state - trivalent. It is recommended to use powerful main filters as treatment plants. This is the equipment with which multilevel filtration is carried out. Each cartridge of the main filter has its own loading - carbon, mesh, membrane. The advantages of this method of iron removal:
- acceptable cost of installations;
- good performance;
- simple installation and maintenance that even beginners can handle.
It is advisable to select washing filters that can be used an unlimited number of times by the method of flow-through processing of the mesh or with the replacement of loads. However, you can buy an inexpensive budget option with a replaceable cartridge - the Aquaphor jug. Its price is from about 350 rubles to 2000. A replaceable cassette allows you to seriously reduce the concentration of iron for 1-2 months (depending on the number of people living in the house).
Catalytic method

The catalytic deferrization of water from a well is a special installation in which Fe2 is oxidized to the trivalent state. More often for this purpose, special fillings are used, which are based on manganese dioxide. In such an environment, iron molecules are oxidized and deposited on the surface of the granules. Then the catalytic charge is flushed, all waste is discharged into the sewer.
This cleaning method has a number of disadvantages:
- Large water consumption for washing the charge, with the help of which it is necessary to regularly clean the backfill layer.
- Low efficiency in relation to organic iron, since it forms a thick film on the surface of the catalytic medium. As a result, the cleaning process is reduced to zero.
- Lack of efficiency at high Fe content in water more than 15 mg / l.
The situation is further aggravated by the presence of manganese impurities in the liquid, which is more difficult to get rid of in parallel with iron.
Electrochemical cleaning method
Water is passed through a special field in which the main ones are the anode and cathode. The result is electrolysis of the liquid. As a result, the volume of the medium is divided into alkaline and acidic. Iron precipitates.
A similar Fe removal method is used in factories and industrial wastewater treatment plants when treating large volumes of water.
Use of reagents

These substances provoke the process of oxidation of iron dissolved in water and its suspension. The following are widely used as reagents:
- hydrogen peroxide;
- sodium hypochlorite.
This method is more often used in industrial wastewater treatment plants, since in addition many large sedimentation tanks are needed for the treated liquid and clarification filters. And it’s not cheap.
The main danger of using reagents in everyday life is the incorrect calculation of dosages, which can lead to dangerous consequences.
Only well-prepared water is suitable for drinking and benefits the body. It is imperative to make a good iron removal filter on a suburban area, even if seasonal residence in the house is supposed.